Living with a loved one who struggles with addiction can expose you to prolonged emotional stress, unpredictability, and even trauma. Over time, these experiences can contribute to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Coping with PTSD in this context involves acknowledging the impact of these experiences, seeking professional treatment, building emotional resilience, and creating safe boundaries. At Sabino Recovery, we specialize in trauma treatment programs designed to help individuals process the complex emotional wounds caused by living in an environment shaped by addiction. With the right therapeutic support, healing and reclaiming a sense of stability is possible.
What is PTSD from Living with an Addict?
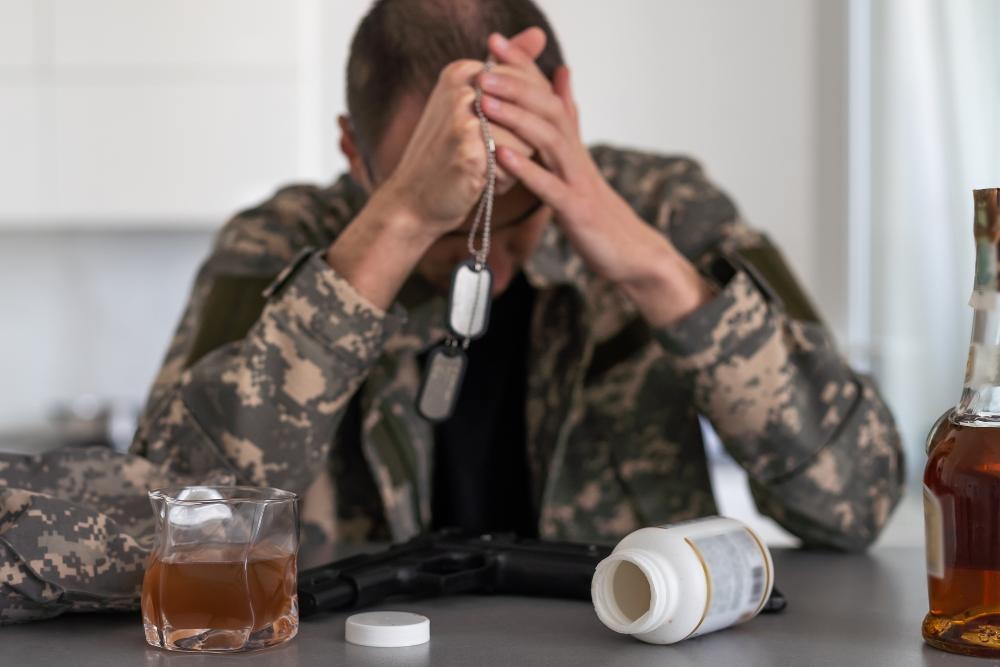

Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). PTSD is a mental health disorder that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. The constant stress and unpredictability of living with an addict can cause trauma, leading to the development of PTSD.
Individuals living with an addict may experience symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and anxiety. They may also feel a constant sense of danger, leading to hypervigilance and an inability to relax. These symptoms can make it difficult to function in daily life and can have a significant impact on mental health.
PTSD from living with an addict can also increase the risk of developing a substance use disorder. Individuals may turn to drugs or alcohol as a coping mechanism to deal with the trauma and stress of living with an addict. This can lead to a vicious cycle of addiction and trauma, making it difficult to break free from either.
It is essential to seek help if you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD from living with an addict. Treatment options such as therapy and medication can help manage symptoms and improve mental health. It is also important to seek support from loved ones and to practice self-care to reduce stress and promote healing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that can lead to the development of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). PTSD is a mental health condition that can occur after someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. If you are living with an addict and experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek professional help.
The symptoms of PTSD can vary from person to person, but some common symptoms include reliving the trauma, avoiding people or places associated with the trauma, negative feelings, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. These symptoms can be severe and can interfere with daily life.
To diagnose PTSD, a mental health professional will conduct a thorough evaluation, including a physical exam and psychological assessment. They will ask about your symptoms and may use diagnostic criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to make a diagnosis.
It is important to note that PTSD can often co-occur with other mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing any symptoms of PTSD, it is important to seek help from a qualified mental health professional. Mental health treatment options may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength and can lead to a better quality of life.
Impact on Different Demographics
PTSD from living with an addict can have a profound impact on different demographics. Here is a breakdown of how it affects various groups:
Men
Men who live with addicts may be less likely to seek help for their PTSD symptoms. They may feel pressure to be strong and stoic, which can make it difficult for them to admit that they are struggling. Men may also be more likely to turn to alcohol or drugs themselves to cope with their PTSD.
Women
Women who live with addicts may be more likely to develop PTSD than men. They may also be more likely to seek help for their symptoms. Women may feel responsible for the addict’s behavior and may experience guilt, shame, and anxiety as a result. They may also be more likely to suffer from depression and other mental health issues.
Children
Children who live with addicts may be at a higher risk for developing PTSD. They may witness traumatic events, such as their parent’s drug use or violent outbursts, which can cause long-term emotional damage. Children may also feel neglected or abandoned by their addicted parent, which can lead to feelings of anger, sadness, and confusion.
Veterans
Veterans who live with addicts may be more likely to develop PTSD than civilians. They may have already experienced trauma during their time in the military, which can make them more susceptible to PTSD from living with an addict. Veterans may also feel a sense of isolation and may struggle to connect with others who have not experienced similar traumas.
Gender
PTSD from living with an addict can impact both men and women, but they may experience different symptoms. Men may be more likely to experience anger and aggression, while women may be more likely to experience anxiety and depression. Both genders may struggle with feelings of guilt, shame, and isolation.
How do Trauma and Abuse Contribute to PTSD in Loved Ones of Addicts?
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience, especially if the addict is a loved one. Witnessing the chaos and destruction caused by addiction can lead to emotional and psychological abuse, which can cause PTSD. Emotional abuse can include verbal attacks, manipulation, and gaslighting. Sexual abuse and assault can also occur in relationships with addicts, leading to further trauma.
PTSD can be triggered by a variety of events, including witnessing a loved one overdose or seeing the aftermath of an overdose. The constant fear of losing a loved one to addiction can cause chronic stress and anxiety, leading to PTSD.
Trauma and abuse can lead to a dysregulated stress system, making individuals more vulnerable to addictive behaviors. Trauma can also lead to depersonalization and numbness, which can increase the risk of addiction as individuals seek to escape their emotions.
It is important for loved ones of addicts to seek support and therapy to address the trauma and abuse they have experienced. Therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies and heal from the emotional wounds caused by addiction.
Treatment and Recovery Options
Living with an addict can be an intensely traumatic experience, and it’s not uncommon for individuals in this environment to develop symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Fortunately, there are effective, evidence-based treatment options that can help you process these experiences and reclaim your well-being. At Sabino Recovery, we specialize in trauma-focused care for individuals impacted by relational trauma and substance-related environments.
Each client at Sabino receives a personalized treatment plan crafted by our multidisciplinary team. This may include advanced therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), EMDR, somatic experiencing, and integrative holistic modalities — all delivered within a private, luxury residential setting. When clinically appropriate, medication management can also support the treatment process.
Our holistic behavioral health programs provide a safe and supportive environment where clients can address both the symptoms of PTSD and the underlying emotional wounds. If you or a loved one is ready to begin the healing journey, Sabino Recovery offers the comprehensive care needed for true transformation.
Support Systems for PTSD Caused by Living with an Addict
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that leaves you with PTSD symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and isolation. However, building a strong support system can help you cope with these symptoms and improve your mental health.
Your support system can include family members, friends, loved ones, and support groups. It is important to have people who are willing to listen to you without judgment and provide emotional support when you need it. You can also consider joining a support group for individuals who have experienced similar situations.
Your support system can help you cope with PTSD symptoms by providing emotional support, practical help, and a sense of belonging. Here are some ways your support system can help you:
- Emotional support: Your loved ones can provide a listening ear, offer words of encouragement, and provide comfort when you are feeling overwhelmed.
- Practical help: Your support system can help you with everyday tasks such as cooking, cleaning, and running errands. This can help reduce your stress levels and allow you to focus on your mental health.
- Sense of belonging: Being part of a support group can provide a sense of belonging and help you feel less isolated. You can share your experiences with others who understand what you are going through.
If your loved one is struggling with addiction, an intervention can be a way to encourage them to seek help. An intervention involves a group of people who are close to the addict coming together to express their concerns and encourage them to seek treatment. This can be a difficult conversation, but it can be an important step towards recovery for both you and your loved one.
Coping with PTSD from Living with an Addict
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that can lead to PTSD. Coping mechanisms and self-care are important for managing the symptoms of PTSD. Here are some ways to cope with PTSD from living with an addict:
What control do you have over your environment?
You may feel like you have no control over your environment when living with an addict. However, there are some things you can do to regain a sense of control:
- Set boundaries: Establishing boundaries can help you feel more in control of your environment. For example, you can set boundaries around drug use or behavior that makes you uncomfortable.
- Create a safe space: Creating a safe space, such as a room in your home, can help you feel more in control of your environment. Make sure this space is free from triggers and reminds you of positive memories.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness can help you feel more in control of your thoughts and emotions. Try incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation or deep breathing, into your daily routine.
How can exercise help with PTSD symptoms?
Exercise can be an effective way to manage PTSD symptoms. Here’s how:
- Releases endorphins: Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. This can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Reduces stress: Exercise can help reduce stress levels, which can be beneficial for managing PTSD symptoms.
- Improves sleep: Exercise can improve sleep quality, which is important for managing PTSD symptoms.
What coping strategies can you use?
Coping strategies are important for managing PTSD symptoms. Here are some coping strategies to try:
- Practice self-care: Self-care is important for managing PTSD symptoms. Make time for activities that you enjoy, such as reading, listening to music, or taking a bath.
- Seek support: Support from friends, family, or a therapist can be helpful for managing PTSD symptoms. Consider joining a support group for people who have experienced trauma.
- Use grounding techniques: Grounding techniques, such as focusing on your breath or using your senses to focus on your surroundings, can help reduce anxiety and other PTSD symptoms.
What is Complex PTSD (CPTSD) and How Does it Relate to Living with an Addict?
Complex PTSD (CPTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing prolonged or repeated trauma, such as living with an addict. CPTSD is characterized by three main symptom clusters: alterations in cognition and mood, alterations in arousal and reactivity, and disturbances in interpersonal relationships.
Alterations in cognition and mood may include symptoms such as negative self-concept, feelings of shame or guilt, and difficulty regulating emotions. Individuals with CPTSD may also experience dissociation, which can manifest as feeling disconnected from oneself or one’s surroundings.
Alterations in arousal and reactivity may include symptoms such as hypervigilance, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. Individuals with CPTSD may also be easily startled or have an exaggerated startle response.
Disturbances in interpersonal relationships may include difficulty trusting others, feeling isolated or disconnected from others, and difficulty maintaining healthy relationships. Individuals with CPTSD may also struggle with boundaries and may have a tendency to become overly enmeshed or avoidant in relationships.
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that can lead to the development of CPTSD. It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of CPTSD. A mental health professional can provide support and guidance in managing symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
How can you Deal with Suicidal Thoughts when Living with an Addict?
Living with an addict can be a traumatic experience that often leads to the development of PTSD. Suicidal thoughts are a common symptom of PTSD that can be triggered by the stress and anxiety of living with an addict. It is essential to seek help and support to manage suicidal thoughts effectively. Here are some tips to help you deal with suicidal thoughts when living with an addict:
Identify Safe Places to Go
Identify several places you can go where you would be less likely to hurt yourself, such as public places like the mall, a coffee shop or restaurant, a busy park, a community center, or a gym. Once there, immerse yourself in that environment. Pay attention and be mindful of all the sights and sounds around you.
Reach Out for Help
It is essential to reach out for help when you are experiencing suicidal thoughts. Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or healthcare professional. You can also call a suicide prevention hotline or seek help from a support group. Remember that you are not alone, and there are people who care about you and want to help.
Practice Self-Care
Taking care of yourself is crucial when dealing with suicidal thoughts. Make sure to get enough sleep, eat a healthy diet, and exercise regularly. Engage in activities that you enjoy, such as reading a book, watching a movie, or spending time with friends. Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, to help reduce stress and anxiety.
How can therapists help individuals with PTSD from living with an addict?
Therapy can be a crucial component in the treatment of PTSD from living with an addict. A therapist can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to work through their emotions and develop coping strategies.
One of the main roles of a therapist is to help individuals process their emotions related to the trauma. This can involve identifying and acknowledging difficult emotions such as anger, guilt, and shame. By working through these emotions, individuals can begin to heal and move forward.
Another important role of a therapist is to help individuals develop healthy ways of coping with their symptoms. This can involve teaching relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and other self-care strategies. Additionally, a therapist can help individuals identify and address any self-medicating behaviors that may be exacerbating their symptoms.
Therapists can also provide support and guidance as individuals navigate the challenges of living with an addict. This can involve helping individuals set boundaries, develop communication skills, and build a support network.
Sabino Recovery Can Help
Recovering from PTSD caused by living with an addict requires more than surface-level coping skills — it involves a comprehensive therapeutic approach that addresses the emotional, relational, and physical effects of trauma. At Sabino Recovery, our trauma treatment program offers a safe, luxury environment where clients can fully engage in deep healing work. If you’re ready to take the next step, exploring our admissions process and insurance verification is an excellent place to begin.