Understanding Trauma
What is trauma, and how does it affect someone? Trauma is a response to a distressing or disturbing event that overwhelms a person’s ability to cope. Trauma can be caused by a variety of events, such as natural disasters, accidents, violence, or abuse. Trauma can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or post-traumatic stress (PTS), which are conditions that can develop after someone has experienced a traumatic event.
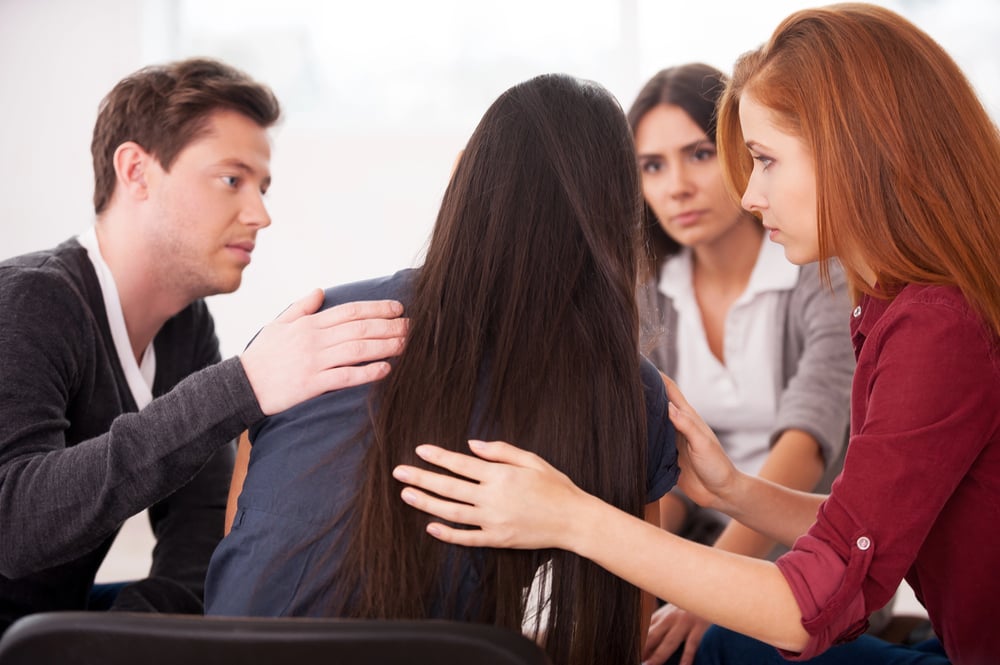

PTSD and PTS can cause a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, and avoiding reminders of the traumatic event. Trauma can also cause triggers, which are situations, people, or things that remind the person of the traumatic event and can cause them to feel anxious, scared, or overwhelmed.
It’s important to understand that trauma can affect people differently, and not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop PTSD or PTS. However, trauma can have a significant impact on a person’s life, and it’s essential to provide support to those who have experienced trauma. Learning about trauma and its effects is crucial to understanding how to support someone with trauma.
Secondary trauma is another type of trauma that can occur when someone is exposed to the trauma of others, such as first responders or healthcare workers. It’s essential to recognize the signs of secondary trauma and provide support to those who are experiencing it.
Dissociation is a response to trauma, where the person may feel disconnected from their thoughts, feelings, or surroundings. It’s important to recognize the signs of dissociation and provide support to those who are experiencing it.
Loss is also a common outcome of trauma, whether it’s the loss of a loved one, a home, or a sense of safety and security. It’s important to acknowledge and validate the person’s feelings of loss and provide support as they navigate their grief.
Recognizing the Impact of Trauma
What are some common feelings that someone who has experienced trauma might have? Trauma can have a significant impact on someone’s mental health, leading to feelings of anxiety, anger, and sadness. It is not uncommon for those who have experienced trauma to feel overwhelmed, and they may struggle with nightmares or flashbacks.
It is important to recognize that trauma can leave emotional scars that may not be visible. Someone who has experienced trauma may not always be able to articulate what they are feeling, and it is important to be patient and understanding.
PTSD is a common mental health condition that can develop after experiencing trauma. Symptoms of PTSD can include intrusive thoughts, avoidance behaviors, and hyperarousal. If someone you know is experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is important to encourage them to seek professional help.
It is also important to recognize that trauma can lead to thoughts of suicide. If someone you know is experiencing suicidal thoughts, it is crucial to take their feelings seriously and seek help immediately.
How can you provide emotional support to someone with trauma?
When someone you care about has experienced trauma, it can be difficult to know how to provide emotional support. However, offering support and comfort can make a significant difference in their recovery process. Here are some ways you can provide emotional support to someone with trauma:
Listen actively: Allow the person to express their feelings and thoughts without interruption. Listen actively and show that you are present and engaged by making eye contact, nodding, and using encouraging words.
Offer comfort: Provide comfort by offering a hug, pat on the back, or a reassuring touch. Let them know that you are there for them and that they are not alone.
Be patient and understanding: Trauma can affect people in different ways, so it’s essential to be patient and understanding. Allow the person to take their time and process their emotions at their own pace.
Respect their boundaries: Respect their need for space and privacy. Let them know that you are available to listen when they are ready to talk.
Avoid judgment: Avoid making assumptions or judgments about their experience. Instead, show empathy and compassion.
Provide social support: Encourage the person to seek social support from others, such as family, friends, or a support group. Social support can help them feel less isolated and provide a sense of belonging.
Offer practical help: Offer practical help, such as running errands or providing meals. Practical help can alleviate stress and allow the person to focus on their recovery.
Remember, providing emotional support to someone with trauma takes time and effort. It’s essential to be patient, understanding, and compassionate. By offering your support, you can make a significant difference in their recovery process.
Encouraging Professional Help
If someone you know and care about has experienced trauma, you may want to encourage them to seek professional help. While it can be difficult to broach the subject, it is important to remember that seeking professional help is a sign of strength and can be a crucial step towards healing. Here are some ways you can encourage someone with trauma to seek the help they need:
- Start by expressing your concern for their well-being. Let them know that you care about them and that you are worried about their health and safety.
- Explain that trauma can have lasting effects on mental health and that seeking professional help is a way to address these effects and promote healing.
- Offer to help them find a therapist or counselor who specializes in treating trauma. You can provide them with resources, such as online directories or referrals from friends or family members.
- If they are hesitant to seek help, remind them that therapy is a safe and confidential space where they can talk about their experiences without fear of judgment or reprisal.
- Encourage them to consider joining a support group or attending counseling sessions with a trusted friend or family member. This can provide additional support and encouragement as they navigate the healing process.
What kinds of professional help are available for someone with trauma? There are several types of professional help that can be beneficial for someone with trauma, including:
- Therapy: This can include talk therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other forms of psychotherapy that are designed to help individuals process their trauma and develop coping strategies.
- Support groups: These can provide a safe and supportive environment where individuals can connect with others who have experienced similar traumas.
- Counseling: This can include individual or couples counseling, and can help individuals work through issues related to their trauma and develop healthy relationship skills.
Why is professional help important for someone with PTSD? Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a serious mental health condition that can develop after someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. While some individuals are able to recover from PTSD on their own, others may require professional help to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Therapy, support groups, and counseling can all be effective treatments for PTSD, and can help individuals develop healthy coping strategies and improve their overall well-being.
Whether someone is experiencing PTSD or another form of trauma, encouraging them to seek professional help can be a powerful way to support their healing journey. Remember to approach the subject with care and compassion, and to provide resources and support as needed.
Understanding and Managing Trauma Triggers
What are trauma triggers and how can you manage them? Trauma triggers are cues that remind someone of a traumatic event, causing them to experience intense emotions and physical sensations. These triggers can be anything from a specific smell or sound to a certain location or situation. Understanding what triggers someone’s trauma can be the first step in managing it.
One way to manage trauma triggers is to help the person feel in control. Encourage them to identify their triggers and develop coping strategies that work for them. This can involve breathing exercises, grounding techniques, or seeking support from a therapist or support group.
It’s important to remember that managing trauma triggers is not the responsibility of the person who experienced the trauma alone. As a supporter, you can help by creating a safe and supportive environment, listening without judgement, and respecting their boundaries.
There are also various treatments available that can help manage trauma triggers, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). These treatments can help someone reprocess their traumatic memories and develop new coping skills.
How can you promote self-care and coping mechanisms for someone with trauma?
Self-care and coping mechanisms are essential for someone with trauma to manage their symptoms and regain a sense of control over their life. Here are some ways you can promote self-care and coping mechanisms for someone with trauma:
Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms can help someone with trauma manage their symptoms and feel more in control. Some effective coping mechanisms include mindfulness, meditation, exercise, and choice. Encourage the person to find what works best for them and to make it a regular part of their routine.
Exercise
Exercise can be an effective way to manage symptoms of trauma. Encourage the person to engage in activities they enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or yoga. Exercise can help them feel more in control of their body and reduce feelings of anxiety and stress.
Safety
Safety is essential for someone with trauma to feel secure and in control. Encourage the person to create a safe space for themselves, whether it’s a physical space or a mental space. Help them identify triggers and develop strategies to manage them.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness can help someone with trauma stay present and focused on the present moment. Encourage the person to practice mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing, visualization, or body scanning. These techniques can help them feel more grounded and in control.
Self-Care
Self-care is essential for someone with trauma to feel valued and cared for. Encourage the person to engage in activities they enjoy, such as reading, taking a bath, or spending time with loved ones. Encourage them to prioritize their needs and to take care of themselves first.
Navigating Relationships Post-Trauma
How can you navigate relationships with someone who has experienced trauma? Trust and communication are key components of any relationship, but they become even more important after trauma. Trauma can affect family life, leading to resentment and other negative emotions. It’s important to be a trustworthy and supportive partner or friend to help your loved one through their recovery.
One of the most important things you can do is to listen to your loved one. Trauma survivors may want to talk about their experiences, but they may also feel hesitant or ashamed. Encourage them to share their feelings and experiences, but don’t push them if they’re not ready. Be patient and understanding.
It’s also important to be mindful of your own emotions and reactions. Seeing someone you care about in pain can be difficult, but it’s important to remain calm and supportive. Try to avoid judgment or criticism, and instead offer your love and support.
Finally, remember to take care of yourself as well. Supporting someone through trauma can be emotionally draining, so it’s important to take time for yourself to recharge. Make sure to practice self-care and seek support from others when you need it.
Whether it’s a romantic relationship, a friendship, or a family bond, navigating relationships post-trauma can be challenging. But with patience, understanding, and open communication, you can help your loved one through their recovery and strengthen your relationship in the process.
How can you support the healing process?
Supporting someone through the healing process after experiencing trauma can be challenging, but it is essential to their recovery. Here are some ways you can help:
Identify Strengths
Remind your loved one of their strengths and positive qualities. This can help build their self-esteem and confidence, which are essential for the healing process. Encourage them to engage in activities that make them feel good about themselves.
Focus on the Future
It is important to help survivors focus on the future and not just the past. Encourage them to set goals and make plans for their future. This can help them feel more in control and optimistic about their life.
Support the Healing Process
Listen to your loved one without judgment and offer emotional support. Help them find a therapist or counselor who specializes in trauma therapy. Encourage them to practice self-care and engage in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction.
Help with the Recovery Process
Be patient and understanding. Recovery takes time, and everyone’s healing journey is different. Celebrate their progress, no matter how small, and encourage them to keep going.
If you or your loved one is struggling with trauma, seek professional help. Remember, healing is possible, and you do not have to go through it alone.