What is Childhood Trauma?
Childhood trauma is a type of trauma that occurs during childhood and can have a lasting impact on a person’s life. Traumatic events can include physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, neglect, natural disasters, accidents, or witnessing violence. Children who experience traumatic events may have difficulty regulating their emotions, forming relationships, and may struggle with mental health issues later in life.
Childhood trauma can be measured using the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) questionnaire, which assesses exposure to different types of traumatic experiences during childhood. The higher the ACE score, the higher the risk for negative outcomes such as substance abuse, depression, and chronic health conditions.
It’s important to understand that childhood trauma is not a choice and can have long-lasting effects on a person’s mental health and well-being. It’s essential to provide support and understanding to individuals who have experienced childhood trauma.
If you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma, seeking professional help can be beneficial in managing symptoms and promoting healing.
Signs and Symptoms of Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Recognizing signs and symptoms can help you support someone with childhood trauma. Here are some common signs and symptoms to look out for:
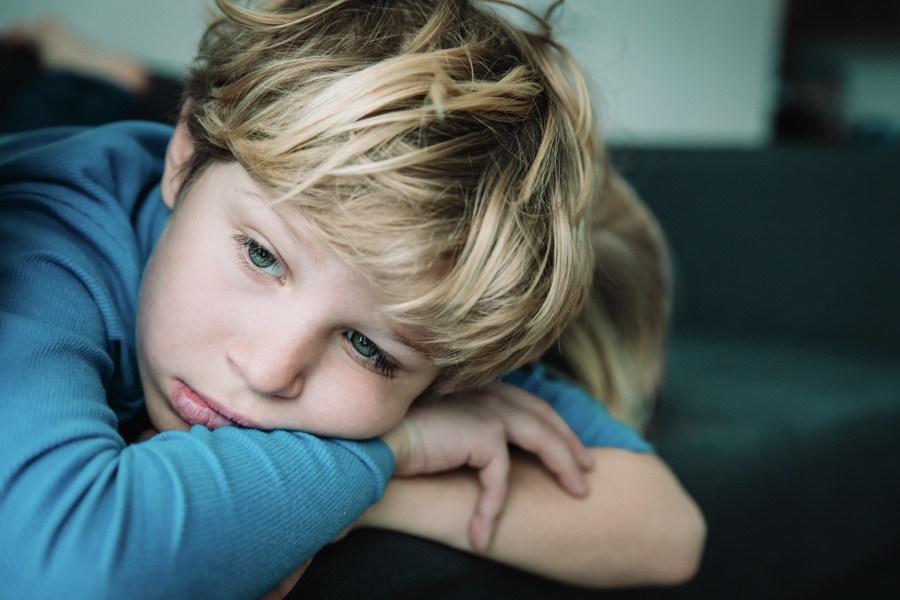

- Emotional distress: Children who have experienced trauma may exhibit a wide range of emotions, including fear, anger, anxiety, numbness, and depression. They may also have difficulty regulating their emotions, leading to outbursts or mood swings.
- Physical symptoms: Trauma can also manifest in physical symptoms, such as headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue. Children may also experience changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
- Behavioral changes: Children who have experienced trauma may exhibit changes in behavior, such as withdrawing from social activities, avoiding certain people or places, or engaging in risky behaviors.
- Nightmares or flashbacks: Trauma can also lead to nightmares or flashbacks, where the child relives the traumatic event.
It’s important to remember that not all children will exhibit the same signs and symptoms of trauma. Some may be more vocal about their experiences, while others may internalize their feelings. If you suspect that a child has experienced trauma, it’s important to approach the situation with sensitivity and empathy. Encourage them to seek professional help and offer your support throughout their healing journey.
Effects of Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma can have long-lasting effects on a person’s mental and physical health. It can lead to emotional distress, depression, and other mental health conditions. It can also impact sleep and appetite, leading to chronic conditions later in life.
Trauma can affect the way a person perceives the world and others around them, leading to difficulties in relationships and social interactions. It can also cause a person to experience flashbacks, nightmares, and other symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Children who experience trauma may have difficulty regulating their emotions and may struggle with impulse control. They may also have difficulty focusing and learning in school.
The effects of childhood trauma can be long-lasting, but with the right support and treatment, it is possible to heal and move forward. It is important to seek help from a mental health professional who is trained in trauma-focused therapy.
If you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma, it is important to remember that healing is possible. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to overcome the effects of trauma and lead a fulfilling life.
How can you support a child with trauma?
If you know a child who has experienced trauma, it’s important to provide them with the right support to help them heal. Here are some tips on how you can support a child with trauma:
One of the most important things you can do is to be there for the child emotionally. Listen to them and validate their feelings. Let them know that what they’re feeling is normal and that you’re there to support them. Encourage them to express their emotions in a safe and healthy way, such as through art or journaling.
Parents and caregivers can provide a safe and stable environment for the child. Establishing routines and structure can help the child feel more secure. Trauma-informed parenting is also important. This involves being aware of how trauma can affect a child’s behavior and responding in a way that is supportive and understanding.
To provide social support, encourage the child to spend time with friends and engage in activities they enjoy. This can help them feel a sense of normalcy and build social skills. Consider connecting them with a support group or a therapist who specializes in trauma.
How can Therapy Help with Childhood Trauma?
Therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals heal from childhood trauma. There are various types of therapy available, but some of the most effective ones include Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR).
CPT is a type of therapy that helps individuals process their traumatic experiences and change negative thoughts and beliefs that may have developed as a result of the trauma. CBT is another type of therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative patterns of thinking and behavior. EMDR, on the other hand, uses eye movements to help individuals process traumatic memories and reduce the intensity of negative emotions associated with them.
Therapy can also help individuals develop coping skills and strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. Additionally, therapy can provide a safe and supportive environment where individuals can explore their feelings and emotions without fear of judgment.
It is important to note that therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and what works for one individual may not work for another. It is crucial to find a therapist who is trained in treating childhood trauma and who you feel comfortable working with.
If you or someone you know is struggling with childhood trauma, seeking therapy can be a crucial step towards healing and recovery.
Coping Strategies and Self-Care
Coping strategies and self-care are essential for supporting someone with childhood trauma. Trauma can be overwhelming, and it is essential to have coping mechanisms to manage the effects of trauma. Here are some strategies that can help:
Coping Strategies
- Encourage the person to talk about their feelings and experiences with someone they trust.
- Help them develop self-soothing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or visualization.
- Encourage them to express their emotions through art, music, or writing.
- Teach them mindfulness techniques to help them stay present in the moment.
- Help them develop a sense of control by setting small, achievable goals.
Self-Care
Self-care is also crucial for someone with childhood trauma. Here are some self-care strategies that can help:
- Encourage them to prioritize their physical health by getting enough sleep, eating healthy foods, and exercising regularly.
- Help them find activities that they enjoy and that help them relax, such as reading, taking a bath, or going for a walk.
- Encourage them to set boundaries and say no to things that are not good for them.
- Help them build a support system of people who understand and care about them.
- Encourage them to seek professional help if needed.
Self-care and coping strategies can help someone with childhood trauma build resilience and learn to manage their symptoms. By supporting them in developing these skills, you can help them on their journey to healing.
Education and Prevention
Prevention and education are essential to help individuals with childhood trauma. By being knowledgeable about the causes and symptoms of trauma, you can avoid triggering events that may exacerbate the condition. Here are some ways that education and prevention can help:
- Prevention: It is important to create a safe environment for individuals with childhood trauma. By implementing a crisis plan for lockdown, lockout, shelter-in-place, or evacuation, you can help to minimize the trauma impact. Additionally, reaffirming the physical health and safety perceptions of the individual can help to prevent further trauma.
- Education: Educating yourself on the impact of childhood trauma can help you to recognize the signs and symptoms. By being knowledgeable about the types of traumatic events and the impact of trauma on children, you can provide the necessary support and care. Additionally, you can help to prevent trauma by being aware of the risk factors and taking steps to mitigate them.
- Safety: Creating a safe environment is crucial for individuals with childhood trauma. By ensuring that their basic needs are met, such as proper nutrition, sleep, and access to medical care, you can help to reduce the risk of triggering events. Additionally, creating a safe space where the individual feels comfortable and secure can help to promote healing.
- Avoidance: Avoiding triggering events is important to prevent further trauma. By being aware of the individual’s triggers and avoiding them, you can help to reduce the risk of retraumatization.
- Knowledge: Being knowledgeable about childhood trauma and its impact can help you to provide the necessary support and care. By understanding the symptoms and the best treatment options, you can help the individual to heal and recover.
Dissociation and Childhood Trauma
Dissociation is a common response to trauma, especially childhood trauma. It is a defense mechanism that allows individuals to disconnect from their thoughts, feelings, body, actions, and surroundings. Dissociation can be difficult to identify, but it is crucial to understand when supporting someone with childhood trauma.
Dissociation can take many forms, including:
- Feeling disconnected from one’s body or emotions
- Feeling like one is watching oneself from outside the body
- Losing time or feeling like time is passing differently
- Feeling like the world isn’t real or feeling like one is in a dream
- Feeling like one is different people at different times
If you are supporting someone who experiences dissociation, it is important to provide a safe and supportive environment. Here are some tips:
- Validate their experiences: Let them know that their experiences are real and that you believe them.
- Be patient: Dissociation can be confusing and scary for the person experiencing it. Give them time and space to process their experiences.
- Help them ground themselves: Encourage them to use grounding techniques, such as deep breathing or focusing on their senses, to help them stay present.
- Avoid triggers: Be aware of potential triggers and help them avoid situations that may cause dissociation.
- Encourage professional help: If their dissociation is impacting their daily life, encourage them to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor.
Understanding dissociation is crucial when supporting someone with childhood trauma. By providing a safe and supportive environment and encouraging professional help, you can help them manage their dissociation and move towards healing.
How Can You Manage Trauma Triggers?
Trauma triggers are events, situations, or images that remind a person of their past traumatic experiences. When triggered, a person may experience intense emotional and physical reactions, such as panic attacks, flashbacks, or dissociation. Managing trauma triggers is crucial to the recovery process of individuals who have experienced childhood trauma. Here are some tips on how you can manage trauma triggers:
- Identify your triggers: Recognizing what triggers you is the first step in managing them. Make a list of your triggers and try to avoid them as much as possible. If avoidance is not possible, prepare yourself for the triggering event by practicing relaxation techniques beforehand.
- Practice grounding techniques: Grounding techniques help you stay present in the moment and prevent you from getting lost in your thoughts or memories. Examples of grounding techniques include deep breathing, meditation, and focusing on your surroundings.
- Seek support: It is important to have a support system in place when dealing with trauma triggers. Reach out to a trusted friend or family member, or consider joining a support group. Professional help from a therapist or counselor can also be beneficial.
- Create a safety plan: A safety plan is a personalized plan that outlines what you can do when you are triggered. It includes coping strategies, emergency contacts, and steps to take if you feel unsafe.
- Practice self-care: Self-care is essential for managing trauma triggers. Engage in activities that make you feel good, such as exercise, hobbies, or spending time with loved ones. Take care of your physical health by eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol.
By implementing these strategies, you can better manage your trauma triggers and take control of your recovery process. Remember that healing from childhood trauma is a journey, and it takes time and effort. Be patient and kind to yourself, and seek help when needed.
Resources for Support
If you know someone who has experienced childhood trauma, it is important to know that there are resources available to help them. Here are some options to consider:
National Child Traumatic Stress Network (NCTSN)
The NCTSN is a network of professionals who provide resources and support for children and families affected by traumatic events. They offer a range of resources, including fact sheets, webinars, and training materials for professionals. They also have a directory of treatment providers that can help connect individuals with trauma-informed care.
SAMHSA’s National Helpline
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) operates a national helpline that provides free, confidential information and referrals for individuals and families facing mental health and substance abuse issues. They can help connect individuals with resources in their area, including trauma-focused treatment options.
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT)
TF-CBT is an evidence-based treatment approach that has been shown to be effective in helping children and adolescents who have experienced trauma. It is a structured therapy approach that focuses on helping individuals process their trauma and develop coping skills.
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR)
MBSR is a mindfulness-based intervention that has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD and improving overall well-being. It involves learning mindfulness meditation and other techniques to help individuals manage their stress and anxiety.
Sabino Recovery
If you or someone you know is struggling with childhood trauma, Sabino Recovery is one of the best PTSD treatment centers in the United States. They offer a range of trauma-focused treatment options, including EMDR, equine therapy, and somatic experiencing. Their team of professionals is dedicated to helping individuals heal from trauma and achieve overall well-being.
Remember, it is important to seek support and resources if you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma. With the right treatment and support, individuals can heal and move forward in their lives.