Understanding Emotional Trauma
What is Trauma?
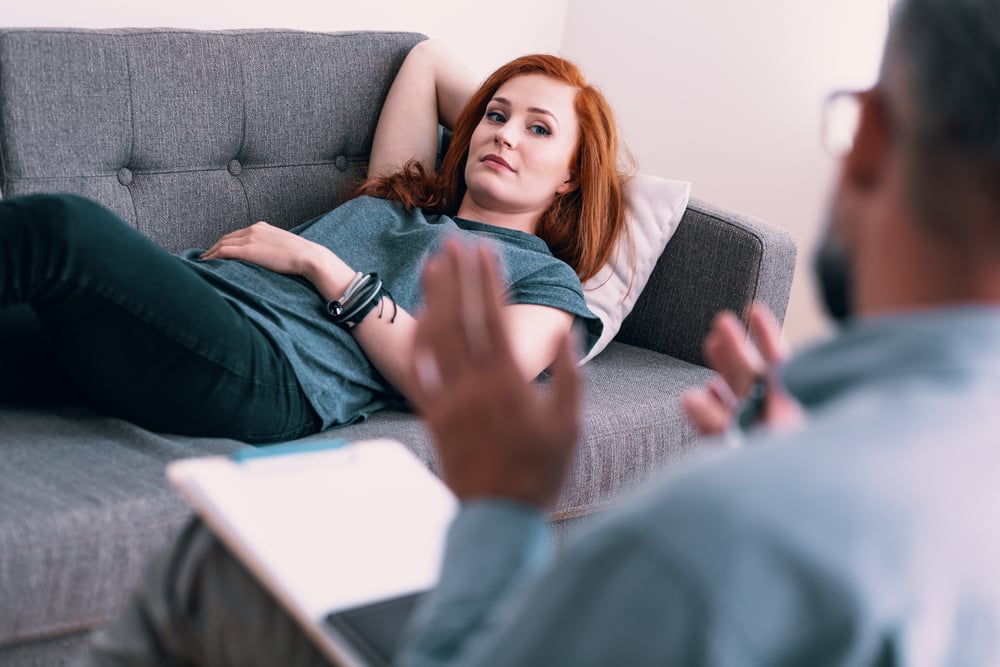

Trauma is defined as a distressing or disturbing experience that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. Trauma can manifest in various forms, ranging from physical injuries to emotional and psychological distress. Traumatic events can occur suddenly and unexpectedly, leaving individuals feeling helpless and powerless. Trauma can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, and recovery can be a long and challenging process.
Types of Traumatic Events
Traumatic events can take many forms, including natural disasters, accidents, abusive relationships, and childhood trauma. Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods can cause physical and emotional trauma. Accidents such as car crashes or workplace injuries can also result in traumatic experiences. Childhood trauma, such as abuse or neglect, can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being.
Physical and Emotional Symptoms
Trauma can cause physical and emotional symptoms that can be debilitating and disruptive to daily life. Physical symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and fatigue can occur immediately after a traumatic event. Emotional symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop over time and interfere with an individual’s ability to function. Symptoms can vary from person to person, and it is essential to seek professional help to manage and treat traumatic stress.
Understanding symptoms is crucial in learning how to help someone with emotional trauma. By providing a safe and supportive environment and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can begin the healing process and work towards recovery.
Effects of Emotional Trauma
Emotional trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health and well-being. It can be caused by a single event or a series of events that overwhelm a person’s ability to cope. Here are some of the effects of emotional trauma:
PTSD and Its Symptoms
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a common result of emotional trauma. It is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Symptoms of PTSD include nightmares, flashbacks, fear, and avoidance. Individuals with PTSD may also experience physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue.
Depression and Anxiety
Emotional trauma can also lead to depression and anxiety. Individuals may feel sad, hopeless, and lose interest in activities they once enjoyed. Anxiety can cause individuals to feel nervous, worried, and on edge. They may also experience physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, and a rapid heartbeat.
Anger and Irritability
Emotional trauma can also cause individuals to feel angry and irritable. They may have difficulty controlling their emotions and may lash out at others. This can lead to problems in personal and professional relationships.
If you or someone you know is experiencing the effects of emotional trauma, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional. With the right treatment, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Have you experienced emotional trauma? Are you struggling with PTSD symptoms, depression, anxiety, anger, or irritability? At Sabino Recovery, we specialize in treating individuals with PTSD and other emotional traumas. Our team of experts can help you develop coping skills and strategies to manage your symptoms. Contact us today to learn more about our programs.
Recognizing Trauma Triggers
If you know someone who has experienced emotional trauma, it is important to recognize the signs of trauma triggers. Trauma triggers can cause sudden changes in behavior and mood, and they can be difficult to predict. Here are some common triggers to look out for:
Intrusive Memories
Intrusive memories are a common symptom of trauma. They can be triggered by anything that reminds the person of their traumatic experience. This can include smells, sounds, or even certain words. If you notice that someone is suddenly quiet or withdrawn, they may be experiencing an intrusive memory.
Sudden Changes
Sudden changes in behavior or mood can be a sign of trauma triggers. If someone suddenly becomes angry or upset, it may be because they have been triggered by something. It is important to be patient and understanding when this happens, as it can be difficult for the person to control their emotions.
Relationship Issues
Trauma can also affect a person’s relationships. If someone is experiencing trauma triggers, they may have difficulty trusting others or may become overly dependent on their loved ones. They may also have difficulty maintaining healthy relationships, which can lead to divorce or other relationship issues.
If you suspect that someone is experiencing trauma triggers, it is important to be supportive and understanding. Encourage them to seek professional help if necessary, and be patient as they work through their emotions. Remember that trauma is a complex issue, and it may take time for the person to fully recover.
Self-Care for Trauma Survivors
If you or someone you know has experienced trauma, it is important to prioritize self-care. Self-care can help reduce stress, improve physical health, and promote emotional well-being. Here are some self-care techniques that may be helpful:
Exercise and Yoga
Regular exercise and yoga can be effective ways to reduce stress and improve physical health. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Yoga can help with relaxation, mindfulness, and flexibility. Consider incorporating yoga or exercise into your daily routine.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Meditation and mindfulness can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Meditation involves focusing your attention on a specific object or activity, while mindfulness involves being present and aware of your thoughts and feelings. Consider practicing meditation or mindfulness for a few minutes each day.
Sleep and Relaxation
Getting enough sleep and practicing relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. Relaxation techniques can include deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or visualization. Consider creating a relaxing bedtime routine and practicing relaxation techniques before bed.
Remember, self-care is not selfish. It is an important part of healing and recovery. By prioritizing self-care, you can improve your physical and emotional well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
If you or someone you know is struggling with emotional trauma, seeking professional help can be an important step towards healing. However, it can be difficult to know when to seek help, what types of therapists are available, and what treatment options are most effective.
When to Seek Help
If you are experiencing symptoms such as anxiety, depression, flashbacks, or nightmares that are interfering with your daily life, it may be time to seek professional help. Additionally, if you have tried self-help techniques such as exercise or mindfulness and are still struggling, it may be time to consider therapy.
Types of Therapists
There are many types of mental health professionals who can provide therapy for emotional trauma. Some common types include psychologists, licensed clinical social workers, and licensed professional counselors. It’s important to find a therapist who is trained in treating trauma and who you feel comfortable working with.
Treatment Options
There are several evidence-based treatments for emotional trauma, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and trauma-focused CBT. These therapies can help you learn coping skills and process traumatic memories in a safe and supportive environment. Other treatment options may include medication, group therapy, or alternative therapies such as art or music therapy.
If you are unsure where to start, there are resources available to help you find a therapist or mental health professional. Your primary care physician may be able to provide a referral, or you can search online for therapists in your area. Remember, seeking professional help is a sign of strength and can help you on your path towards healing.
Support Systems for Trauma Survivors
Trauma survivors often benefit from having a support system in place. Support systems can provide emotional and practical support, help with coping strategies, and reduce feelings of isolation. A good support system can be crucial to a survivor’s recovery. Here are some examples of support systems:
Support Groups
Support groups can provide a safe and non-judgmental space for trauma survivors to share their experiences and feelings with others who have been through similar situations. Support groups can be found through community organizations, mental health clinics, and online resources.
Family and Friends
Family and friends can play a vital role in a survivor’s support system. They can provide emotional support, help with daily tasks, and be a listening ear when needed. It is important for family and friends to be patient and understanding, as trauma survivors may need time and space to heal.
Online Resources
Online resources can provide a wealth of information and support for trauma survivors. Websites, forums, and social media groups can connect survivors with others who have been through similar experiences and offer a sense of community. Online resources can also provide information on coping strategies, self-care, and professional treatment options.
How can you build a strong support system?
Building a strong support system takes time and effort. Here are some tips for building a strong support system:
- Reach out to others who have been through similar experiences
- Join a support group or online community
- Talk to family and friends about your needs and how they can support you
- Seek professional help from a therapist or counselor
- Practice self-care and coping strategies to reduce stress and anxiety
Remember, building a support system is an ongoing process. It is important to prioritize self-care and seek help when needed. With time and effort, a strong support system can help trauma survivors on their journey to recovery.
Coping with Trauma
If you or someone you know has experienced emotional trauma, coping with the aftermath can be a challenging process. However, there are effective ways to manage the symptoms of traumatic stress and begin the healing process. Here are some strategies for coping with trauma:
Dealing with Flashbacks
Flashbacks can be one of the most distressing symptoms of traumatic stress. They can feel overwhelming and make you feel as though you are reliving the traumatic event. To cope with flashbacks, try the following:
- Grounding techniques: focus on your senses and surroundings to bring yourself back to the present moment
- Deep breathing: take slow, deep breaths to calm your body and mind
- Positive self-talk: remind yourself that the traumatic event is in the past and that you are safe now
Managing Anxiety and Fear
Anxiety and fear are common symptoms of traumatic stress. They can be debilitating and interfere with daily life. To manage anxiety and fear, try the following:
- Relaxation techniques: such as meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation
- Exercise: physical activity can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation
- Seeking support: talking to a trusted friend or mental health professional can help you manage anxiety and fear
Overcoming Guilt and Shame
Guilt and shame are common emotions experienced after a traumatic event. It is important to remember that these feelings are a normal response to trauma and that you are not to blame for what happened. To overcome guilt and shame, try the following:
- Self-compassion: treat yourself with kindness and understanding
- Challenging negative thoughts: replace negative self-talk with positive affirmations
- Seeking therapy: a mental health professional can help you work through feelings of guilt and shame
Remember, coping with trauma is a process, and it takes time. Be patient with yourself or your loved one and seek professional help if needed.
Healing from Trauma
If you or someone you know has experienced trauma, it is important to understand that healing is possible. While the journey may be difficult, there are therapeutic techniques that can help with the healing process.
Therapeutic Techniques
There are many therapeutic techniques available to help individuals heal from trauma. Some of these techniques include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A type of talk therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): A type of therapy that uses eye movements to help process traumatic memories and reduce their impact.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): A type of meditation-based therapy that helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts and emotions, and learn to manage them more effectively.
How can you let go of the past and move forward after trauma?
Letting go of the past can be a difficult process, but it is essential for healing from trauma. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Practice self-compassion: Be kind to yourself and acknowledge that healing takes time.
- Connect with others: Surround yourself with supportive individuals who understand what you are going through.
- Focus on the present: Try to stay in the present moment and avoid dwelling on past events.
- Engage in self-care: Take care of your physical and emotional well-being by getting enough sleep, eating well, and engaging in activities that bring you joy.
How can healing from trauma improve your well-being?
Healing from trauma can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. When you are able to process and let go of past traumatic experiences, you may experience:
- Increased feelings of peace and calm
- Improved relationships with others
- Greater self-awareness and self-acceptance
- Increased ability to cope with stress and adversity
If you or someone you know is struggling to heal from trauma, it is important to seek professional help. With the right support and therapeutic techniques, it is possible to heal and move forward towards a brighter future.