Understanding Childhood Trauma
What is childhood trauma? Childhood trauma refers to any experience that a child undergoes that results in physical or emotional harm. It can take many forms, including abuse, neglect, violence, natural disasters, loss of a parent, and car accidents.
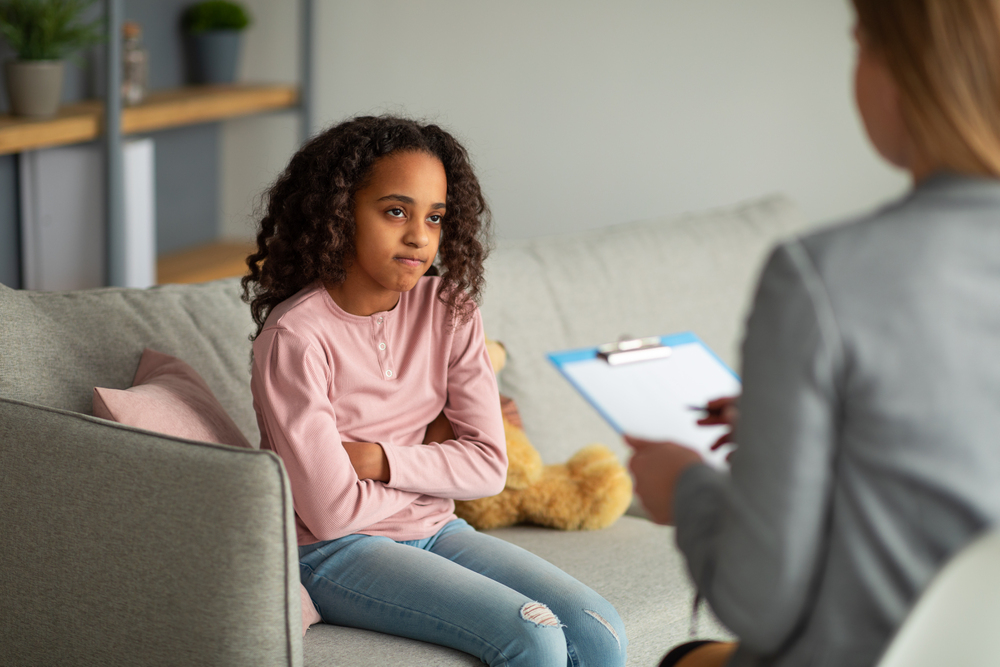

How does childhood trauma lead to addiction? Childhood trauma is a significant risk factor for addiction, as it can lead to the development of coping mechanisms that involve substance abuse. Trauma can also lead to changes in brain chemistry that make individuals more susceptible to addiction.
Different types of childhood trauma can have varying impacts on individuals. Physical abuse, for example, can result in physical harm and emotional distress. Emotional abuse can be just as damaging, leading to long-term mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Neglect is another form of childhood trauma that can have a lasting impact on individuals. Children who experience neglect may struggle with feelings of abandonment and low self-worth, which can lead to substance abuse and other destructive behaviors.
It’s important to note that childhood trauma doesn’t always involve intentional harm. Household dysfunction, such as living with a parent who struggles with addiction, can also be traumatic for children.
Trauma and Its Impact on Children
How does childhood trauma affect children? Trauma experienced during childhood can have a significant impact on a child’s development and mental health. Traumatic events can cause alarm and distress in children and adolescents, leading to a range of symptoms and mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
When children experience trauma, their central nervous system can become overactive, leading to hyperarousal and irritability. Trauma can also cause high levels of stress hormones, which can have long-lasting effects on a child’s mental health and development. These effects can persist well into adulthood, leading to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders and addiction.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of childhood trauma is essential for early intervention and treatment. Children who have experienced trauma may exhibit a range of symptoms, including difficulty sleeping, nightmares, flashbacks, and behavioral problems. If left untreated, these symptoms can lead to more severe mental health problems and addiction.
At Sabino Recovery, we understand the impact that childhood trauma can have on a person’s mental health and well-being. Our team of experienced professionals provides personalized treatment for PTSD and other mental health disorders, helping individuals heal and recover from the effects of trauma.
Link Between Childhood Trauma and Addiction
Have you ever wondered why some people turn to drugs or alcohol to cope with their emotional pain? Childhood trauma is one of the leading causes of addiction and substance abuse.
Studies have shown that individuals who have experienced childhood trauma, such as neglect, physical, sexual, or psychological abuse, grief, witnessing domestic violence, medical traumas, or having a parent that used drugs or was mentally ill, are more likely to develop substance use disorders later in life.
Childhood trauma can lead to self-medication as a way to cope with the emotional pain caused by the traumatic experience. This can result in the development of substance dependence and addiction. The risk of addiction is also higher in individuals who have experienced multiple traumas or have comorbid mental health disorders.
Substance use disorders resulting from childhood trauma can involve a variety of substances, including alcohol, marijuana, nicotine, cocaine, opioids, and cannabis. Individuals with a history of childhood trauma are also more vulnerable to addiction and have a higher risk of suicide attempts and gambling addiction.
If you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma and is struggling with addiction, it is essential to seek professional help from a reputable treatment center like Sabino Recovery to address the underlying issues and promote long-term recovery.
How do Coping Mechanisms Influence Addiction?
Childhood trauma can lead to the development of addiction, and coping mechanisms play a crucial role in this process. Coping mechanisms are the behaviors and strategies people use to deal with stressors and negative emotions. Coping mechanisms can be adaptive or maladaptive, and they can either promote recovery or contribute to addiction.
Maladaptive coping mechanisms, such as escape and avoidance, provide temporary relief from negative emotions but can lead to addiction in the long term. People who use drugs or alcohol to cope with trauma often do so to escape their negative feelings, but this behavior can quickly become compulsive and lead to addiction.
Adaptive coping mechanisms, such as mindfulness and cognitive restructuring, help individuals manage their emotions in a healthy way and promote recovery. Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and observing thoughts and emotions without judgment, while cognitive restructuring involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with positive ones.
In some cases, people may use both adaptive and maladaptive coping mechanisms. For example, someone may use mindfulness to manage their emotions but also use drugs or alcohol to escape them. In these cases, it is important to address both types of coping mechanisms in addiction treatment.
Gender Differences in Trauma and Addiction
Are there gender differences in how trauma leads to addiction? Research suggests that men and women may experience and respond to trauma differently, which can affect their likelihood of developing addiction.
Studies have found that women are more likely to experience sexual abuse and interpersonal violence, which can increase their risk of developing addiction. Women may also be more likely to use drugs to cope with trauma-related symptoms such as anxiety and depression. In contrast, men may be more likely to use drugs to cope with trauma-related anger and aggression.
However, it is important to note that men and women may also experience similar types of trauma, such as physical abuse or neglect, and may develop addiction for similar reasons. Additionally, gender is just one factor that can influence the relationship between trauma and addiction. Other factors, such as age, race, and socioeconomic status, may also play a role.
At the end of the day, it is important to approach each individual’s experience with trauma and addiction on a case-by-case basis, rather than making assumptions based on gender or other demographic factors. By understanding the unique challenges faced by each person, we can provide more effective and personalized treatment for trauma and addiction.
Understanding Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
What are Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)? ACEs are traumatic experiences that children experience before the age of 18 that can have lasting impacts on their mental health, physical health, and general well-being. According to the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study, there are ten types of childhood trauma that are categorized into three groups: abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. The ten types of ACEs are:
- Physical abuse
- Sexual abuse
- Emotional abuse
- Physical neglect
- Emotional neglect
- Substance abuse in the household
- Mental illness in the household
- Domestic violence
- Parental separation or divorce
- Incarcerated household member
It’s important to note that ACEs are not limited to these ten types of trauma. Other types of ACEs can include poverty, discrimination, and community violence.
ACEs can have a profound impact on a person’s life, leading to a variety of negative outcomes such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. In fact, research has shown that there is a strong link between childhood trauma and addiction. Trauma can lead to a dysregulated stress system, which may increase vulnerability to addictive behaviors. Trauma can also lead to depersonalization and numbness, which may similarly increase the risk of addiction.
Preventing ACEs is crucial to reducing the number of adults with depression by as much as 44%. Identifying and preventing ACEs can also have implications for clinical practice and help healthcare providers better understand and treat patients who have experienced childhood trauma.
How do Biological Changes Due to Trauma and Addiction Interact?
Childhood trauma can lead to biological changes that increase the risk of addiction. Trauma can cause changes in neural structure, particularly in the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. These changes can lead to a dysregulated stress response and an inability to regulate emotions, leading to an increased risk of addiction.
One of the key neurotransmitters involved in addiction is serotonin. Serotonin is involved in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep, and low levels of serotonin have been linked to depression and anxiety. Childhood trauma can lead to decreased levels of serotonin, which can lead to an increased risk of addiction.
In addition to changes in neural structure and serotonin levels, trauma can also lead to changes in gene expression. Trauma can cause epigenetic changes, which can alter the expression of genes involved in stress response and addiction.
Options for Treating Childhood Trauma and Addiction
Treating childhood trauma and addiction can be a complex process that requires professional help. There are several options available for individuals who are seeking treatment and recovery from the effects of trauma and addiction.
Therapy
Therapy is an effective treatment option for individuals who have experienced childhood trauma and are struggling with addiction. Therapy can help individuals identify and address the root causes of their addiction, develop coping skills to manage triggers, and improve their overall mental health. Behavioral therapy, in particular, has shown to be effective in treating trauma and addiction.
Rehab
Rehabilitation centers provide a structured and supportive environment for individuals who are seeking treatment for trauma and addiction. Rehab programs offer a range of services, including counseling, and group therapy. Clinicians at rehab centers can provide trauma-informed care and a trauma-informed approach to addiction treatment.
Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial for individuals who have experienced childhood trauma and are at risk of developing addiction. By seeking professional help early on, individuals can address the underlying issues that contribute to their addiction and prevent further harm. Early intervention can include therapy, behavioral therapy, and mental health treatment.
Partners
Partners can play an important role in supporting individuals who are seeking treatment for trauma and addiction. Partners can provide emotional support, help with daily tasks, and attend therapy sessions with their loved one. Partners can also participate in family therapy to address any issues that may have contributed to the trauma and addiction.
How do Social and Environmental Factors Contribute to Addiction?
Childhood trauma can create a ripple effect that extends beyond the individual and into their social and environmental surroundings. The social and environmental factors that surround an individual can contribute to addiction in a variety of ways.
One social factor that can contribute to addiction is domestic violence. Children who grow up in households where domestic violence is present are at a higher risk of developing addiction later in life. The trauma and stress associated with domestic violence can lead to a dysregulated stress system, which may increase vulnerability to addiction.
Attachment issues can also contribute to addiction. Children who grow up in households where they do not form secure attachments with their caregivers are at a higher risk of developing addiction. The absence of a secure attachment can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can be a contributing factor to addiction.
Natural disasters can also contribute to addiction. Children who experience natural disasters may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which can increase their risk of developing addiction later in life. The trauma associated with natural disasters can lead to a dysregulated stress system, which may increase vulnerability to addiction.
Finally, cultural norms and media representation can also contribute to addiction. Children who grow up in environments where drug and alcohol use is normalized may be more likely to develop addiction later in life. Additionally, media representation of drug and alcohol use can also contribute to addiction by normalizing and glamorizing substance use.
The Role of Psychiatry in Trauma and Addiction
How does psychiatry play a role in understanding and treating the link between childhood trauma and addiction?
Research shows that childhood trauma can lead to a variety of psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, major depression, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These disorders can increase the risk of developing substance abuse and addiction later in life.
Psychiatrists can help identify and treat these underlying psychiatric disorders, which can help reduce the risk of addiction. They can use a variety of techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and medication management, to help patients manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of relapse.
At Sabino Recovery, we offer a comprehensive approach to treating trauma and addiction. Our team of psychiatrists, therapists, and other healthcare professionals work together to provide personalized care that addresses the unique needs of each patient. We use evidence-based treatments and holistic therapies to help patients heal from the effects of trauma and addiction.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction or the effects of childhood trauma, we encourage you to seek help from a qualified mental health professional. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to overcome these challenges and live a healthy, fulfilling life.