Understanding Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma can have long-lasting effects on a child’s brain development and mental health. Trauma can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical abuse, sexual abuse, emotional neglect, and bullying.
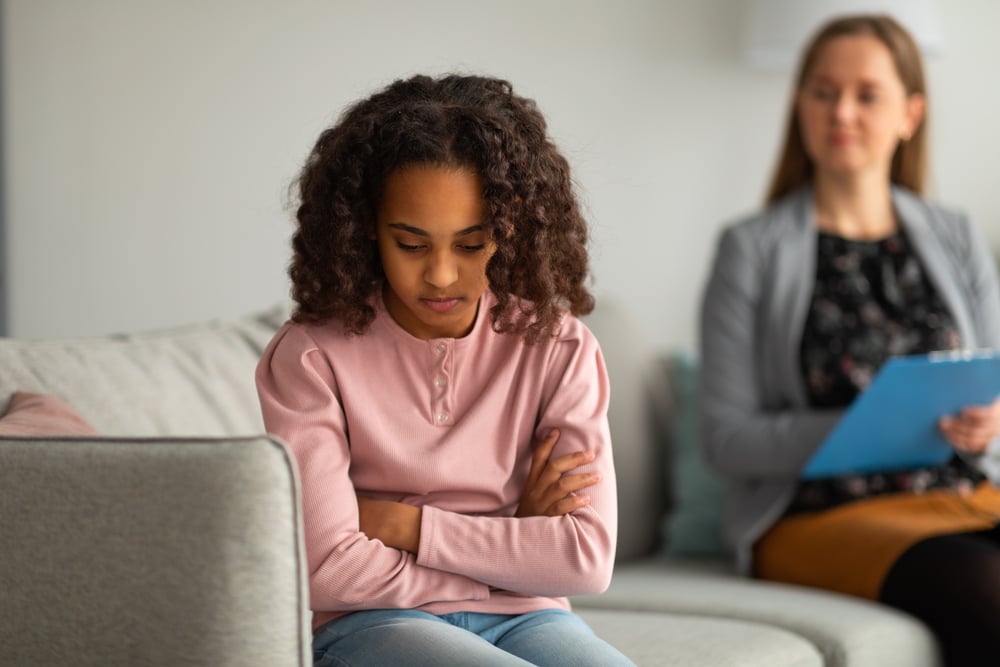

Children who experience trauma may have difficulty regulating their emotions, which can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. They may also struggle with memory, attention, and learning, which can impact their academic performance.
How does childhood trauma affect the brain? Research has shown that childhood trauma can have physical effects on the brain, including changes in brain structure and function. These changes can lead to problems with processing emotions, making decisions, and regulating behavior.
It’s important to understand that not all children who experience trauma will develop mental health problems, but it’s important to provide support and resources for those who do. Early intervention and treatment can help mitigate the effects of trauma and improve outcomes for children.
If you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma, it’s important to seek help from a mental health professional. There are many effective treatments available, including therapy, medication, and other forms of support.
What is childhood trauma?
Childhood trauma refers to experiences that are emotionally or physically harmful to a child. These experiences can include abuse, neglect, violence, and other forms of trauma.
Trauma can have long-lasting effects on a child’s mental health, including increased risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. It can also affect brain development, leading to problems with attention, memory, and learning.
Different types of childhood trauma
There are many different types of childhood trauma, including physical abuse, sexual abuse, emotional neglect, and bullying. Each type of trauma can have unique effects on a child’s mental health and brain development.
Physical abuse refers to any form of physical harm inflicted on a child, such as hitting, kicking, or shaking. Sexual abuse involves any form of sexual contact between an adult and a child. Emotional neglect refers to a lack of emotional support or attention from a caregiver. Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior towards a child by another child or group of children.
How can childhood trauma be prevented?
Preventing childhood trauma requires a multi-faceted approach that involves addressing the root causes of trauma, providing support for families and children, and promoting positive mental health.
Some strategies for preventing childhood trauma include promoting healthy relationships and communication within families, providing resources and support for families experiencing stress or hardship, and implementing policies and programs to address issues like poverty, violence, and abuse.
Long-term effects of childhood trauma
The long-term effects of childhood trauma can be significant, including increased risk of mental health problems, physical health problems, and social and economic problems.
Children who experience trauma may struggle with mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and PTSD. They may also have physical health problems like chronic pain, heart disease, and diabetes. Socially, they may struggle with relationships, employment, and other aspects of life.
How can childhood trauma be treated?
Childhood trauma can be treated through a variety of approaches, including therapy, medication, and other forms of support. Therapy can help children and families address the emotional and psychological effects of trauma, while medication can help manage symptoms like anxiety and depression.
Other forms of support, like support groups and community programs, can also be helpful for children and families coping with trauma. It’s important to seek help from a mental health professional if you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma.
The Brain and Childhood Trauma
Brain Imaging Techniques
Brain imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans have been used to study the effects of childhood trauma on the brain. These techniques allow us to see changes in brain structure and function that may be related to traumatic experiences. For example, studies have shown that childhood trauma is associated with changes in the size and activity of the amygdala, which is involved in processing emotions such as fear and anxiety. Other studies have found that trauma can affect the development of the prefrontal cortex, which is important for decision-making and impulse control.
Impact of Childhood Trauma on Brain Structures
Childhood trauma can have long-lasting effects on the developing brain. Studies have shown that trauma can lead to changes in the structure and function of multiple stress-sensitive areas, including the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex (PFC), and the amygdala. For example, trauma can lead to a reduction in cortical thickness in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and frontoparietal regions, which are important for emotional regulation and attention. Trauma can also lead to a reduction in the volume of the hippocampus, which is involved in memory and learning.
Emotional Impact of Childhood Trauma
Emotion Processing
Childhood trauma can have a profound impact on the way you process emotions. Studies show that individuals who experienced childhood trauma are more likely to have difficulty identifying, expressing, and regulating their emotions. They may also have a heightened sensitivity to emotional stimuli, which can lead to feelings of fear, anxiety, and sadness.
Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation is the ability to manage and control your emotions in a healthy and adaptive way. Childhood trauma can make it difficult to regulate your emotions, leading to mood swings, impulsivity, and difficulty coping with stress. Individuals who experienced childhood trauma may also struggle with low self-esteem and have a greater need for emotional support and validation.
Research has shown that childhood trauma can have long-lasting effects on emotional development, leading to a greater risk for mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. It is important to seek professional help if you are struggling with the emotional impact of childhood trauma.
Addressing the Emotional Impact of Childhood Trauma
There are a variety of evidence-based treatments available to help individuals address the emotional impact of childhood trauma. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), can help individuals process and reframe traumatic experiences, develop healthy coping strategies, and improve emotion regulation skills.
In addition to therapy, self-care practices such as mindfulness, exercise, and healthy sleep habits can also help improve emotional well-being. It is important to prioritize emotional needs and seek support from loved ones and mental health professionals when needed.
If you or someone you know is struggling with the emotional impact of childhood trauma, it is never too late to seek help and begin the journey towards healing and recovery.
Cognitive Consequences of Childhood Trauma
IQ and Cognitive Development
Childhood trauma can negatively impact cognitive processing, leading to problems with problem-solving and decision-making. Studies have shown that individuals who experienced childhood trauma may have lower IQ scores and exhibit slower cognitive development compared to those who did not experience trauma. Trauma can also lead to difficulties with attention, memory, and learning, which can further impact cognitive development.
Memory
Trauma can have a significant impact on memory. Individuals who experienced childhood trauma may have difficulty recalling specific details of the traumatic event, while also experiencing intrusive memories or flashbacks. This can lead to difficulties with attention and concentration, as well as problems with short-term memory. Trauma can also impact autobiographical memory, making it difficult for individuals to accurately recall important life events.
Mental Health and Childhood Trauma
PTSD and Childhood Trauma
Do you know that childhood trauma can lead to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)? PTSD is a mental health condition that develops after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. Childhood trauma is one of the leading causes of PTSD. Children who experience trauma may develop PTSD symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and intense anxiety.
It is important to note that not all children who experience trauma develop PTSD. However, the risk of developing PTSD increases with the severity of the trauma and the child’s age. Early intervention and treatment can help reduce the risk of developing PTSD.
Dissociation and Trauma
Have you heard of dissociation? Dissociation is a common response to trauma. It is a coping mechanism that helps people disconnect from their thoughts, feelings, and memories. Children who experience trauma may dissociate as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions and memories associated with the trauma.
Dissociation can manifest in different ways, such as feeling numb, spacing out, or feeling like you are watching yourself from a distance. While dissociation can be a helpful coping mechanism in the short term, it can become problematic if it persists and interferes with daily functioning.
Therapy can help children who dissociate due to trauma learn healthy coping mechanisms and process their emotions and memories in a safe and supportive environment.
What are Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)?
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood and can have lasting impacts on a person’s mental and physical health. These experiences can include violence, abuse, neglect, and growing up in a family with mental health or substance use problems. ACEs can also be related to natural disasters or other threatening events.
Research has shown that ACEs can lead to toxic stress, which can affect brain development and how the body responds to stress. This can increase the likelihood of developing mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). ACEs can also lead to chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences ACEs will develop negative outcomes. Resilience and protective factors, such as having a supportive caregiver or positive relationships, can help mitigate the effects of ACEs.
If you have experienced ACEs, it’s important to seek support and treatment to help manage the impact of these experiences on your life. Sabino Recovery, one of the best PTSD treatment centers in the United States, offers specialized treatment for individuals who have experienced traumatic events in childhood. Their trauma-informed care approach can help individuals heal from the effects of ACEs and develop healthy coping skills.
Treatment and Intervention Strategies
Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches for childhood trauma focus on helping children develop coping skills and resilience to manage their symptoms. Evidence-based therapies, such as Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT), Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), are effective in treating childhood trauma. Exposure therapy, in which children are gradually exposed to the traumatic event in a safe and controlled environment, can also be helpful.
Family therapy can be an essential part of treatment, as it can help improve communication and strengthen relationships among family members. It can also provide a safe space for children to process their trauma and receive support from loved ones.
Medication and Treatment
Medication can be helpful in managing symptoms of childhood trauma such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medication, and mood stabilizers are commonly prescribed for children with trauma-related symptoms. However, medication should be used in conjunction with therapy and other forms of treatment.
Early intervention is crucial for children with trauma-related symptoms. The earlier children receive treatment, the better their chances of recovery. It is essential to find a qualified mental health professional who has experience working with children and trauma.
If you are seeking treatment for childhood trauma, it is essential to find a treatment center that provides evidence-based therapies and a comprehensive approach to treatment. Sabino Recovery is one of the best PTSD treatment centers in the United States and offers a range of therapies and treatments to help children heal from trauma.
Role of Caregivers and Relationships
The Importance of Secure Attachment
How important is a secure attachment between a child and their caregiver? A secure attachment is crucial to a child’s development because it provides a safe and stable environment for them to grow and learn. When a child feels secure in their relationship with their caregiver, they are more likely to explore the world around them, develop healthy coping strategies, and form positive relationships with others. On the other hand, a lack of secure attachment can lead to emotional and behavioral problems, including anxiety, depression, and difficulty forming relationships with others.
The Role of Caregivers in Healing
What is the role of caregivers in healing childhood trauma? Caregivers play a critical role in helping children heal from trauma. They can provide emotional support, help children develop healthy coping strategies, and provide a safe and stable environment for them to grow and learn. In fact, research has shown that caregivers who are supportive and involved in their child’s treatment can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Caregivers can also benefit from therapy themselves, as they may be dealing with their own trauma or mental health issues related to their child’s trauma.
Prevention and Public Health Response
Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies for childhood trauma are crucial to reducing the likelihood of children experiencing traumatic events. Some prevention strategies include educating parents and caregivers on how to create safe and stable environments for children, promoting positive parenting techniques, and providing access to mental health services. Additionally, community-based prevention programs can help reduce the impact of poverty and other social determinants of health that can contribute to childhood trauma.
Public Health Initiatives
There are several public health initiatives aimed at addressing childhood trauma. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network (NCTSN) is a resource for children and families affected by trauma. The NCTSN provides training and technical assistance to professionals who work with children and families, and promotes the development of evidence-based treatments for trauma. Other public health initiatives include increasing awareness of childhood trauma, improving access to mental health services, and supporting research on the impact of trauma on children and young adults.
If you are looking for a treatment center that specializes in PTSD, Sabino Recovery is one of the best in the United States. Sabino Recovery offers a variety of evidence-based treatment options, including trauma-focused therapy and experiential therapies. Sabino Recovery also provides a safe and supportive environment for individuals to heal and recover from trauma.