Overview of Alcoholic Jaundice Eyes
Alcoholic jaundice is a condition that affects your liver due to excessive alcohol consumption. It occurs when the liver struggles to process alcohol and, as a result, causes a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment and is responsible for the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, commonly associated with jaundice.
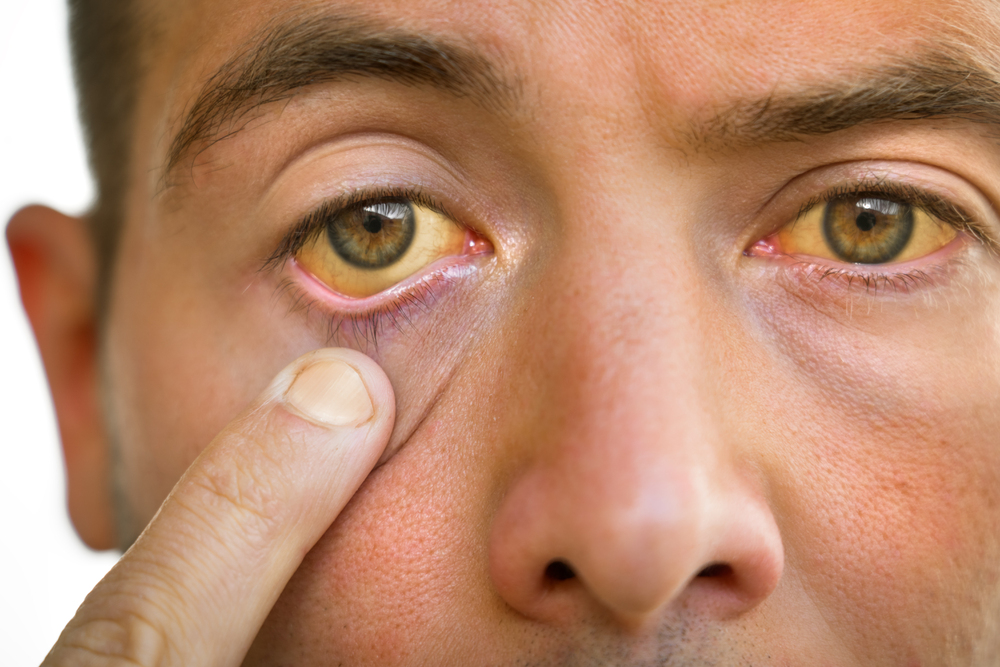
There are several symptoms to look out for with alcoholic jaundice, including:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes: This is the most noticeable symptom and could be more challenging to see on Black and brown people.
- Loss of appetite: You may not feel hungry or might find it difficult to eat.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can occur due to the liver’s inability to process toxins.
- Abdominal tenderness and pain: You may experience discomfort in the area around your liver.
- Tiredness and weakness: These are common symptoms due to the liver’s decreased ability to function properly.
The severity of alcoholic jaundice depends on the extent of liver damage. Prolonged heavy alcohol use can cause inflammation and scarring of the liver, known as cirrhosis. By reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption, you can give your liver a chance to recover and decrease the risk of developing severe liver diseases or complications.
To prevent alcoholic jaundice, it is crucial to monitor your alcohol intake and seek help if you find it challenging to control your drinking. Regular medical checkups and liver function tests can also help identify any issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. Remember, taking care of your liver is essential for maintaining overall good health.
How Does Drinking Alcohol Harm Your Liver?
What Happens to Your Liver?
When you consume alcohol, your liver works to break it down and eliminate it from your body. However, the liver can only process a certain amount of alcohol at a time, and excessive consumption can lead to liver damage. The main culprit behind this damage is a toxic byproduct called acetaldehyde, which is produced when alcohol is metabolized. Acetaldehyde can cause inflammation, oxidative stress, and the production of harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS), ultimately leading to liver injury.
How Does Inflammation and Hepatitis Develop?
As your liver becomes damaged due to alcohol consumption, it may develop inflammation. This inflammation occurs in a condition called alcoholic hepatitis, which is characterized by the death of liver cells and subsequent scarring. Some common symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include:
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, called jaundice
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Belly tenderness
- Fever, often low grade
- Tiredness and weakness
These symptoms result from the liver’s reduced ability to perform its essential functions, such as cleansing the blood, producing bile, and regulating blood clotting.
When Does Cirrhosis Occur?
If alcohol consumption continues and is not properly managed, alcoholic hepatitis can progress to alcoholic cirrhosis – the most advanced and irreversible form of liver injury. Cirrhosis involves the widespread destruction of normal liver tissue, replacing it with scar tissue. This scarring impairs the liver’s ability to function efficiently, leading to an increased risk of life-threatening complications like liver failure or internal bleeding.
To minimize the risk of developing liver complications like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, it is crucial to limit alcohol consumption, follow a balanced diet, and seek professional help if struggling with alcohol addiction. Remember, taking care of your liver is essential for maintaining your overall health and well-being.
Factors Contributing to Alcoholic Jaundice
Alcohol Consumption Patterns
Excessive alcohol consumption plays a significant role in the development of alcoholic jaundice. Heavy drinking and binge drinking put your liver under constant stress, causing it to produce more bilirubin, which leads to the appearance of yellow eyes. It’s crucial to monitor and control your alcohol intake to prevent this condition.
Genetic and Demographic Factors
Some genetic and demographic factors contribute to the risk of developing alcoholic jaundice. Research has shown that women are more susceptible to alcohol-induced liver damage than men, which might be due to differences in the way alcohol is metabolized. Additionally, certain racial groups and individuals with specific genetic factors may have a higher risk of developing alcoholic liver disease, which can lead to jaundice.
Related Health Conditions
Alcoholic jaundice often occurs alongside other health conditions that impact the liver. Obesity is one such factor, as it can cause fatty liver disease, worsening liver damage caused by alcohol. Furthermore, if you have pre-existing liver conditions, such as hepatitis, your liver’s ability to process bilirubin might already be compromised, making you more prone to jaundice when consuming alcohol excessively.
To lower your risk of developing alcoholic jaundice, focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and controlled alcohol consumption. Remember, your liver plays a critical role in your overall health, so it’s essential to take care of it.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Identifying Symptoms
You may notice that the most common sign of alcoholic jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. This could be harder to see on people with darker skin tones. In addition to jaundice, other symptoms include fever (often low grade), nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and weight loss. You might also experience confusion, belly tenderness, and tiredness.
Blood Tests and Imaging
Your doctor will likely perform blood tests to check for signs of liver dysfunction and increased bilirubin levels. Normal serum levels of bilirubin are less than 1mg/dL; however, jaundice is best appreciated when levels reach more than 3 mg/dL. Blood tests can also reveal disturbances in clotting factors, indicating a risk of bleeding.
In some cases, imaging tests such as CT scans can provide additional information about your liver’s condition, including potential swelling or evidence of advanced liver disease. A liver biopsy might be performed to examine a sample of liver tissue and confirm the diagnosis.
Assessing Liver Function
It’s crucial to evaluate your liver function to determine the severity of your condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. A thorough medical history will be taken, including information about your alcohol consumption habits. Doctors use this information to assess the implications of your symptoms and test results on your overall liver health. Possible scenarios can range from mild alcoholic hepatitis to severe liver failure, requiring different interventions and care.
Complications of Alcoholic Jaundice
Liver Failure and Cancer
Alcoholic jaundice can lead to serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. Long-term excessive alcohol consumption damages your liver cells, which can eventually cause liver failure. Liver cancer is another possible complication of alcoholic jaundice. It is essential to monitor your liver function and seek medical help if you notice signs of these complications like abdominal pain, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Ascites and Kidney Failure
Another complication of alcoholic jaundice is ascites — a condition in which fluid accumulates in your abdominal cavity. This can lead to kidney failure, as your kidneys have difficulty processing the excess fluid. To minimize the risk of ascites and kidney failure, it is essential to manage your alcohol consumption and receive appropriate treatments for alcoholic jaundice.
Varices and Hepatic Encephalopathy
Varices, or swollen blood vessels in your esophagus or stomach, can result from the increased pressure in your liver caused by alcoholic jaundice. This may lead to life-threatening internal bleeding. Hepatic encephalopathy, a decline in brain function, is another possible complication. It occurs when toxins accumulate in your brain due to your liver’s inability to remove them adequately. Symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy include changes in your mental state, personality, and behavior.
By addressing your alcohol consumption and seeking appropriate medical help, you can take steps to prevent or manage the complications associated with alcoholic jaundice. With proper care and support, you can improve your liver health and avoid these dangerous consequences.
Treatment and Management Options for Alcoholic Jaundice Eyes
Lifestyle Modifications and Diet
Making lifestyle changes can significantly help in the treatment and management of alcoholic jaundice eyes. Adopting a healthy diet with a focus on reducing fat intake can help alleviate the symptoms of fatty liver disease. Including more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources in your diet is advisable. It is essential to abstain from alcohol consumption, as it can worsen the condition.
Medications and Therapies
Medications can be prescribed by healthcare professionals to help manage alcohol use disorder and treat the underlying causes of jaundice. Anti-anxiety or antidepressant medications may be used to ease withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, therapies such as counseling and support groups can prove beneficial in addressing addiction and promoting abstinence from alcohol.
Liver Transplant Considerations
In severe cases of alcoholic jaundice eyes, where the liver functions are severely compromised, a liver transplant may become necessary. However, this is typically considered only after exhausting all other treatment options and when the patient demonstrates a commitment to maintaining sobriety. The transplant process involves rigorous evaluation and a search for a compatible donor liver, followed by a surgical procedure to replace the damaged liver with the healthy donor liver. Recovery from a liver transplant can be a lengthy process, requiring continued medical monitoring and adjustments in medication.
Please remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations on treatment options for alcoholic jaundice eyes based on your specific situation and needs.
Preventive Strategies and Education for Alcoholic Jaundice
Preventing alcoholic jaundice begins with making informed choices about alcohol consumption. Following the guidelines set by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) can help maintain a healthier lifestyle and avoid the risks associated with heavy drinking.
Moderate drinking, as defined by NIAAA, is one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. Sticking to these limits may reduce the likelihood of developing alcoholic jaundice and other alcohol-related complications.
To further educate yourself, consider participating in programs or workshops focusing on alcohol awareness and healthy drinking habits. Some key points to keep in mind in order to prevent alcoholic jaundice are:
- Always consume alcohol in moderation
- Avoid binge drinking
- Track your alcohol intake and drink within recommended guidelines
- Seek professional help for alcohol use disorder, if needed
Understanding the risks and taking preventive measures can make a significant difference in promoting overall health and reducing the occurrence of alcoholic jaundice. Stay informed and make responsible choices regarding alcohol consumption.


